OVERVIEW
Brain aneurysm is the bulging or ballooning of a blood vessel supplying the brain. Brain aneurysms are present in 1 to 2% of the population. Those aged 40-60 years are most likely to be affected.
SYMPTOMS
- Headaches
- Double vision
The most serious complication is bursting or rupturing of the aneurysm that leads to severe sudden episodes of headache and immediate death in up to 20% of affected patients. In the remaining affected population, it leads to serious haemorrhagic stroke that is potentially debilitating if left untreated.
RISK FACTORS
Some of the known risk factors include:
- Family history
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Age over 50 years.
DIAGNOSIS
A simple CT scan or an MRI scan is all that is needed to diagnose a brain aneurysm and plan treatment.
OUR TREATMENT
Brain aneurysms are a treatable condition and the best time to treat it is before it ruptures.
Coiling is a minimally invasive technique and a common alternative to the traditional open surgery method of clipping.
- Coiling may be balloon or stent assisted.
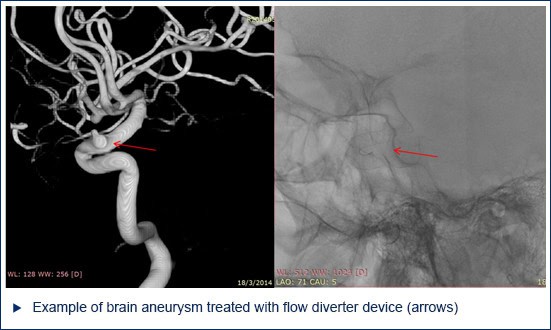
- Another method is to use a special flow diverter stent to treat the aneurysm.
- Involves a small incision in the groin to access a blood vessel.
- Small catheters and wires are put through the incision and directed to the brain to block off the aneurysm.
- The treatment time and length of recovery period are both much shorter than open surgery (1-2 days if the aneurysm is unruptured).