The Importance of the Body’s Lymphatic System
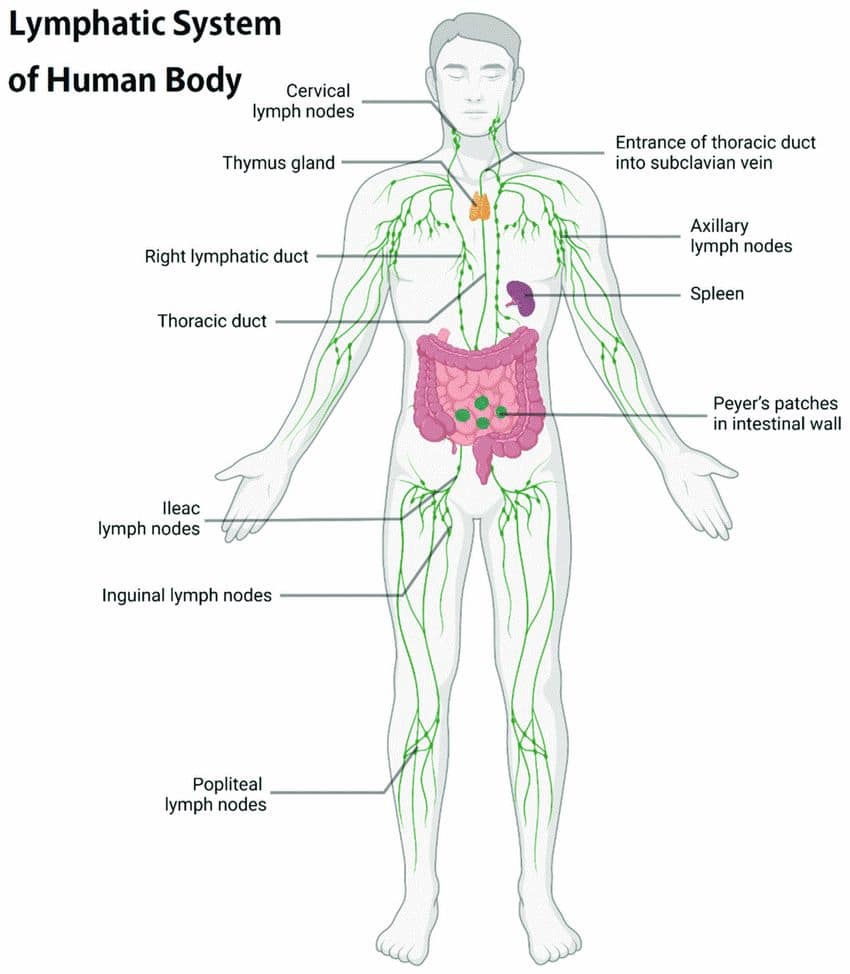
The lymphatic system, often referred to as the body’s “sewage system,” plays a fundamental role in sustaining our overall health and equilibrium. It operates as a vigilant regulator of fluid levels within our body tissues, efficiently collecting and transporting excess fluids that escape from our blood vessels. This process is essential for sustaining the proper balance of fluids in our body, ensuring tissues receive essential nutrients and oxygen while averting the potential consequences of fluid accumulation, such as swelling and tissue damage. It actively filters out harmful pathogens from lymph fluid, partaking in the general immune response, while also coordinating the actions of immune cells and antibodies to combat precise threats.
(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362318010_Nanomaterial-Based_Drug_Delivery_System_Targeting_Lymph_Nodes/figures?lo=1)
Introduction to Lymphoedema
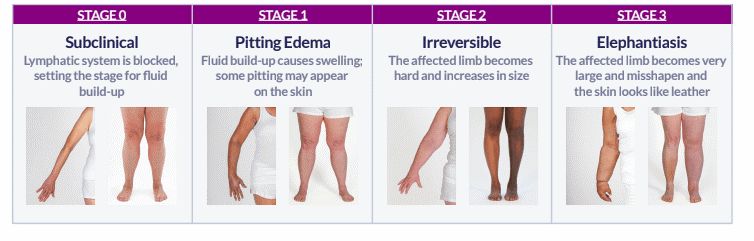
Lymphoedema is a condition characterized by tissue swelling due to the buildup of protein-rich fluid, usually drained through the lymphatic system. While it commonly affects the limbs, it can also impact other body areas. Lymph nodes, which filter lymph fluid and are vital components of the lymphatic system, can be damaged or removed during cancer treatments, leading to lymphoedema. This condition can hinder limb movement, increase the risk of infections, and cause skin problems. Treatment options include compression therapy, massage, pneumatic pumping, skin care, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions to alleviate swelling or create alternative drainage pathways. Lymphoedema treatment is readily accessible in Singapore.
(https://www.lymphaticdrainage.co.nz/lymphoedema)
Symptoms of Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema manifests through various symptoms that primarily involve swelling, which can affect different parts of the body. Swelling often occurs in the arms and legs, including the fingers and toes, as well as in the head and neck region. This swelling can lead to a persistent feeling of heaviness and aching in the affected areas, accompanied by a tightening of the skin. Individuals with lymphoedema may also experience fatigue and fluid leakage through the skin. The condition can further hinder basic movements, making tasks more challenging. Additionally, due to impaired lymphatic drainage, there is a heightened risk of more frequent infections and the development of chronic wounds, which underscores the importance of timely diagnosis and appropriate management.
Causes and Types of Lymphoedema
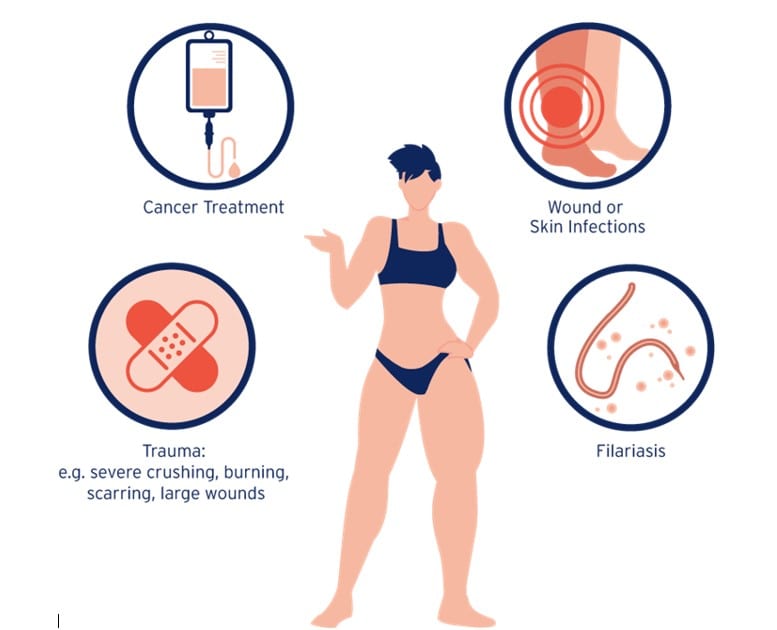
Lymphoedema can arise from various causes and risk factors, categorized into primary and secondary lymphoedema. Primary lymphoedema, although rare, typically results from congenital absence or the failure of the lymphatic system to function properly from birth. In some cases, individuals may present with swollen limbs at birth, while others may experience symptoms during their teenage years, indicating delayed primary lymphatic failure.
On the other hand, secondary lymphoedema is more common and often occurs because of medical interventions or conditions. Surgery, particularly lymph node removal during procedures like breast cancer surgery and axilla lymph node clearance, can disrupt lymphatic drainage, leading to secondary lymphoedema. Similarly, radiation therapy targeting lymph nodes in areas like the groin or pelvis can also damage the lymphatic system. Additionally, recurrent skin infections, such as cellulitis, have the potential to impair lymphatic drainage, contributing to the development of secondary lymphoedema. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for both diagnosis and management of lymphoedema.
(https://www.lymphcare.com/na-en/what-is-lymphedema/causes-and-types-of-lymphedema/)
Risk Factors of Lymphoedema
Several risk factors contribute to the development of lymphoedema. Firstly, advancing age plays a role, as the lymphatic system experiences natural degeneration with age, diminishing its efficiency in managing lymphatic fluid. Additionally, unhealthy body weight and obesity pose significant risks, as fat exerts pressure on lymphatic vessels, impairing their ability to drain lymph, and in some cases, leading to complete obstruction. In rare instances, lymphoedema can emerge as a complication of certain inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid, adding another layer of complexity to its potential causes.
Diagnosis of Lymphoedema
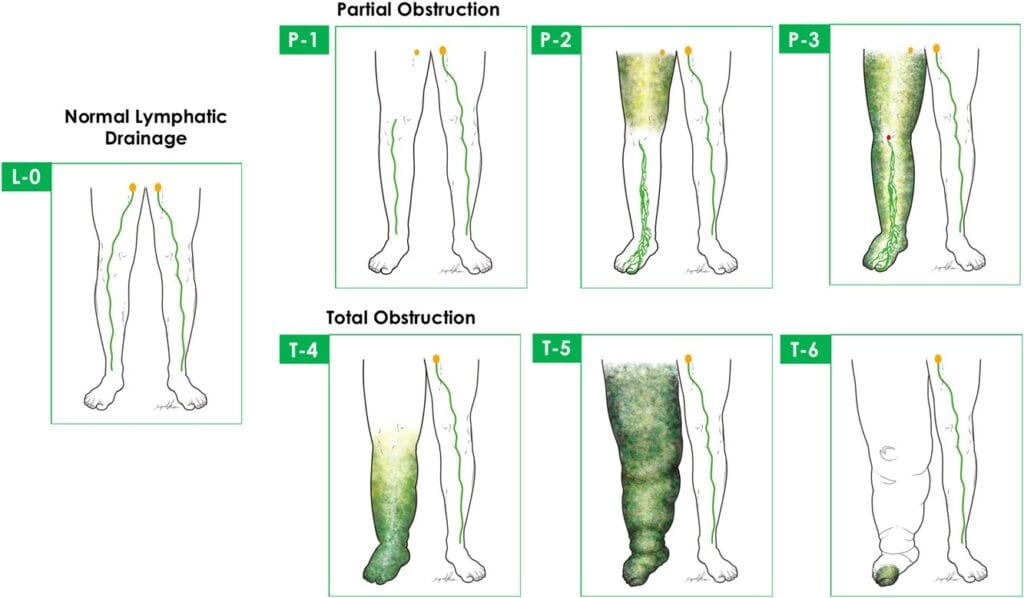
Diagnosing lymphoedema involves a comprehensive process that includes several key steps. First and foremost, obtaining a detailed medical history is essential, focusing on the duration of limb swelling. It is crucial to exclude other potential causes of limb swelling, such as underlying vein diseases, muscle and soft tissue infections, or recent injuries. To further refine the diagnosis and distinguish between primary and secondary lymphoedema, as well as assess the extent of the condition, a specialized imaging test called lymphoscintigraphy may be conducted. This thorough diagnostic approach ensures an accurate assessment and appropriate management of lymphoedema.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jso.25526)
Treatment Options for Lymphoedema
In addressing lymphoedema, the primary objective of treatment is to alleviate limb swelling and restore optimal functionality. Two components of this treatment approach are lymphatic drainage massage and compression dressings, which have demonstrated significant effectiveness in reducing swelling. However, it’s important to note that both of these treatments require regular and consistent application.
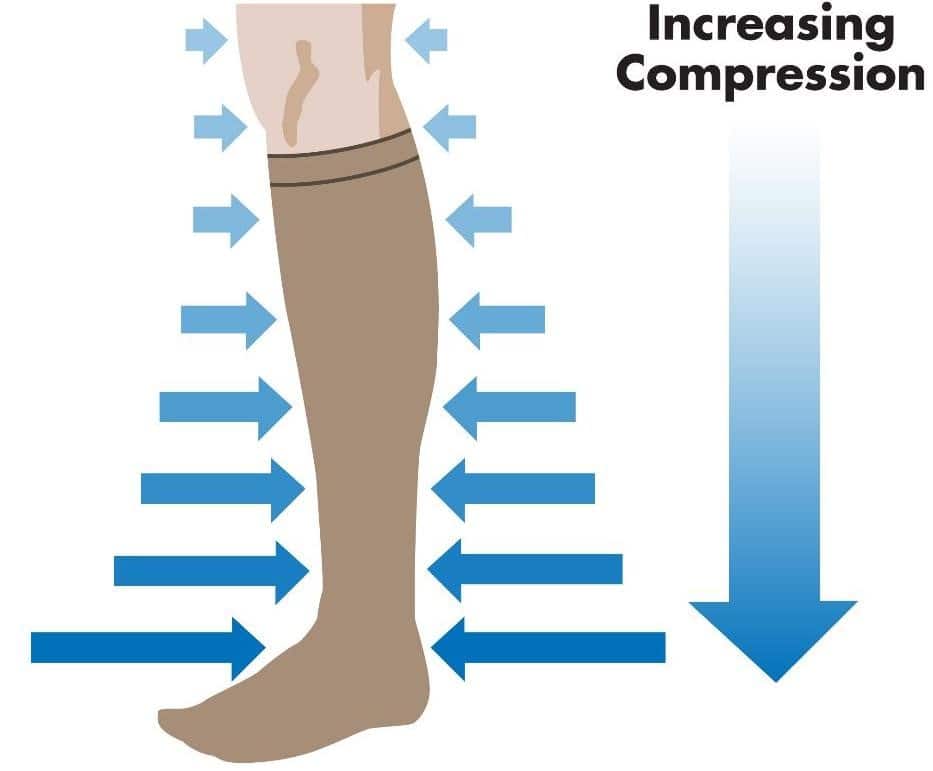
(https://www.pebbleuk.com/graduated-compression/)
In recent years, there have been advancements in the treatment of lymphoedema. These newer therapies encompass surgical interventions aimed at improving lymphatic drainage. This involves surgically connecting blocked lymph drainage channels to small veins, a technique known as lymphovenous bypass. Additionally, lymph node transplants to the affected limb have emerged as another option. These surgical interventions offer promising avenues for enhancing the management of lymphoedema.
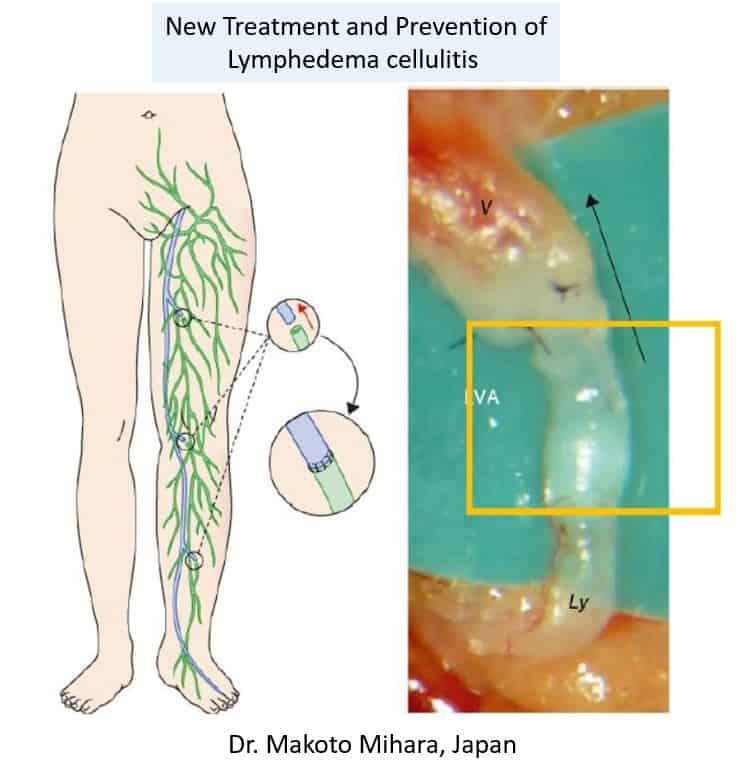
(https://www.english-mominoki-shinryosho.net/lva-lymphatic-venous-anastmosis/)
Benefits of Lymphoedema Treatment
Seeking treatment for Lymphoedema offers several significant benefits. Left untreated, Lymphoedema can result in the gradual and progressive swelling of affected tissues, which can become increasingly uncomfortable and limit mobility. However, undergoing appropriate treatment can effectively alleviate this pain and reduce swelling, significantly improving an individual’s overall quality of life. Moreover, treatment can help minimize the risk of recurrent and potentially serious infections, which are common complications of untreated Lymphoedema. In Singapore, many individuals grappling with Lymphoedema have experienced these advantages firsthand, underscoring the value and importance of seeking and benefiting from Lymphoedema treatment.
Health Implications of Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema can potentially lead to a range of health issues. First, it heightens the risk of infections in the swollen area as the body’s infection-fighting cells struggle to access and protect that specific region. Additionally, wounds in areas affected by Lymphoedema may exhibit delayed healing. Emotionally, Lymphoedema can evoke feelings of distress, depression, embarrassment, or anger. Furthermore, the joints in the affected body part might become stiff or painful. These combined effects underscore the importance of managing and seeking treatment for Lymphoedema to mitigate these potential health challenges.
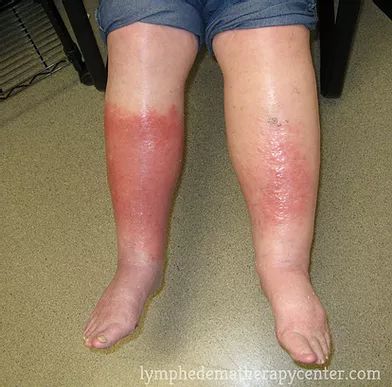
(https://www.compasstherapeutic.com/stages-of-lymphedema/)
Management & Lifestyle Considerations for Lymphoedema
Effective management of Lymphoedema revolves around two key principles: preventing infections and facilitating the unobstructed flow of fluids through the swollen area. To prevent infections, it’s crucial to maintain skin hygiene by keeping it clean and adequately moisturized. In the event of a minor cut or abrasion, prompt cleaning, the application of antibacterial ointment, and securing with a bandage are essential precautions. Avoiding needle sticks, such as vaccines or blood tests, in the swollen area is also imperative to minimize infection risks.

(https://www.lymphatica.com.au/lymphoedema-management)
In terms of promoting unrestricted fluid flow, it’s advisable to steer clear of tight-fitting clothing or jewelry that might constrict lymphatic pathways. If Lymphoedema affects one arm, it’s advisable to have blood pressure measurements and blood drawn from the unaffected arm. Additionally, when experiencing swelling in an arm or leg, elevating it above heart level whenever possible can aid in fluid drainage and alleviate symptoms associated with Lymphoedema. These proactive measures are essential components of a comprehensive strategy for effectively managing Lymphoedema and enhancing overall well-being.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor about Lymphoedema Treatment
- What is the underlying cause of my lymphedema?
- What are the available treatment options for my lymphedema?
- How can I prevent infections and complications related to lymphedema?
- Are there lifestyle changes or exercises that can help manage my lymphedema?
- What can I expect in terms of long-term management and prognosis?
Remember that open and honest communication with your vascular surgeon is crucial for effective lymphedema management. These questions can serve as a starting point for a conversation about your condition and its treatment for your well-being.
Finding the Right Lymphoedema Specialist in Singapore
The Vascular & Interventional Centre has a team of quality vascular surgeons, well-versed in endovascular and surgery treatments for all vascular-related diseases. Our team of specialist doctors and staff strive to provide patients with holistic care in a fully integrated clinic and Day Surgery Centre for a wide variety of vascular conditions. You can contact us at +65 6694 6270 (WhatsApp) or send us an email at en*****@sg***********.com.
FAQs
Lymphoedema is a condition characterized by tissue swelling due to the buildup of protein-rich fluid, often stemming from lymphatic system disruptions. It can impact various body areas, hinder limb movement, increase infection risk, and prompt skin issues. Treatment options range from compression therapy to surgical interventions, with accessible treatment options available in Singapore.
The Vascular & Interventional Centre in Singapore has a team of vascular surgeons and staff experienced in various vascular-related diseases and treatments. They offer a wide range of services at their integrated clinic and Day Surgery Centre. Contact them at +65 6694 6270 (WhatsApp) or via email at en*****@sg***********.com.
Lymphoedema manifests through swelling in different body parts, including limbs, head, and neck. Symptoms include aching, skin tightening, fatigue, and fluid leakage. It can limit mobility and increase infection risk. Timely diagnosis and management are crucial.
Lymphoedema treatment aims to reduce limb swelling and enhance functionality through methods like lymphatic drainage massage and compression dressings. Recent advancements include surgical interventions like lymphovenous bypass and lymph node transplants, offering promising avenues for management.
Seeking lymphoedema treatment provides several advantages, including reduced swelling, improved mobility, and lower infection risk. Treatment can significantly enhance overall quality of life, highlighting its importance for individuals in Singapore dealing with lymphoedema.
References
- https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/survivors/patients/lymphedema.htm
- https://www.sgvascularctr.com/service/lymphoedema/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lymphoedema/

Dr Chen Min Qi profile
Dr. Chen Min Qi is a fellowship-trained Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon who graduated from the National University of Singapore in 2005. He subsequently completed his basic and advanced training in General and Vascular Surgery while obtaining the Member of Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (MRCSed) qualification in 2010, and the Master of Medicine (General Surgery) qualification in 2015. Dr Chen was subsequently successful at the fellowship exams obtaining the Fellow of Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (FRCSed) qualification in 2016.
Upon completion of his advanced surgical training, Dr Chen Min Qi joined the newly opened Ng Teng Fong General Hospital (NTFGH) as a specialist in the Vascular Surgery division. In 2018, Dr Chen was awarded the Health Manpower Development Plan (HMDP) grant from MOH to undergo further subspeciality Vascular training at the internationally renowned St Mary’s Hospital in London, United Kingdom. There Dr Chen gained further experience in surgeries on complex abdominal and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms, redo open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms following failed EVAR surgeries as well as carotid endarterectomy surgery and lower limb revascularization surgeries.
Upon his return in 2020, Dr Chen Min Qi joined the newly formed Woodlands Health as head of their Vascular service, before joining his current practice at the Vascular and Interventional Centre in January 2023.
